Predicting soil erosion
Conventional soil erosion models are generally based on the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), or a revised (RUSLE) or modified (Williams and Berndt (1977)) version of the USLE. Betrie et al (2011) used the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), which uses MUSLE to compute soil erosion, to model sediment transport in the Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. However, one of the challenges with these models is that they generally do not represent gully erosion well (if at all), and that very few data-sets are available for validating the modeled erosion rates, making it difficult to assess the quality and accuracy of the modeled outputs. Also, they do not accurately model the source areas for erosion, which is where interventions need to be targeted to reduce erosion rates.
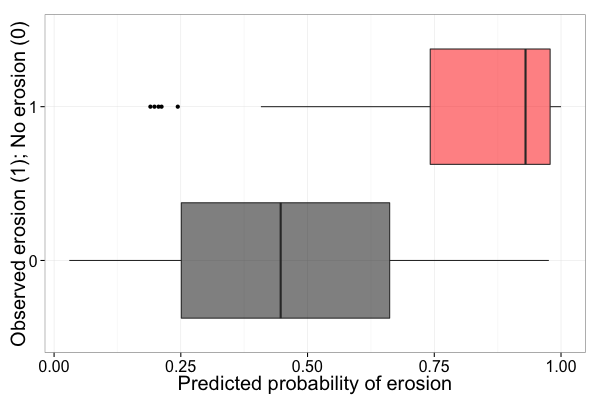
We present an approach to the modeling and mapping of soil erosion that is based on extensive field surveys using the Land Degradation Surveillance Framework (LDSF) in the Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Overall accuracy of the prediction model is about 85%, when using an independent data-set for validation. The resulting map (see below) shows the predicted erosion prevalence in % for each MODIS pixel within the basin. The full map can be accessed here (for registered users).
References
Betrie, G.D., Mohamed, Y.A., Van Griensven, A., Srinivasan, R., 2011. Sediment management modelling in the Blue Nile Basin using SWAT model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 15, 807–818. doi:10.5194/hess-15-807-2011
Williams, J. and Berndt, H.: Sediment yield prediction based on watershed hydrology, T. ASAE, 20, 1100–1104, 1977.

Comments
No comments yet.